1 概要
使用Spring框架,我们需要了解Bean的创建加载过程,需要熟悉Bean是如何获取和使用的。 下面我们通过分析下Spring加载XML文件的过程来分析Bean的数据流。 当前调试的Spring 版本是最新的 4.1.0 release 版本
调试代码主入口
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("consumer.xml");
System.out.println("Consumer Started");
ConsumerBean bean = context.getBean(ConsumerBean.class);
String secretKey = bean.getProperties().getProperty("SecretKey");
System.out.println(secretKey);
2 解析过程
创建 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象,会调用refresh()方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// 获取xml文件的信息,存储在beanFactory对象中
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
.................省略中间代码
// 注册bean信息
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 实例化bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
之后会进入AbstractApplicationContext对象,处理如下方法:
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//初始化DefaultListableBeanFactory对象和DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry对象
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
接下来的数据调用链: getBeanFactory() –> loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象用于解析xml
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//载入xml信息
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
最终会进入loadBeanDefinitions()方法,来载入xml
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
使用EncodeResource封装资源文件。如指定编码则使用指定编码读取资源 判断该资源是否已经加载过 构造InputStream实例,然后调用 doLoadBeanDefinitions() 方法
解析XML文件内容,得到一个Document对象
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//通过dom框架解析成Document对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//缓存每个bean的信息
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
}
封装成BeanDefinition对象过程
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
//获取bean标签元素
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
最终处理的方法
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
........省略
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
" with a framework-generated bean definition ': replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
}
else {
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
最后xml的的信息会存入DefaultListableBeanFactory的private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap对象中
在执行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法和finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)方法的时候,会将beanDefinitionMap中的信息实例化具体bean对象,其主要过程如下:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames;
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
}
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
............................
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
缓存Bean的过程
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
在 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry中private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects属性中缓存bean对象
3 获取Bean
方法调用链如下: getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType) –> doGetBean(name, requiredType, args, false) –> Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName)
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
获取bean方法就很明显了,默认的单例对象,会在singletonObjects中获取
4 Bean生命周期
Spring Bean 的生命周期状态图如下:
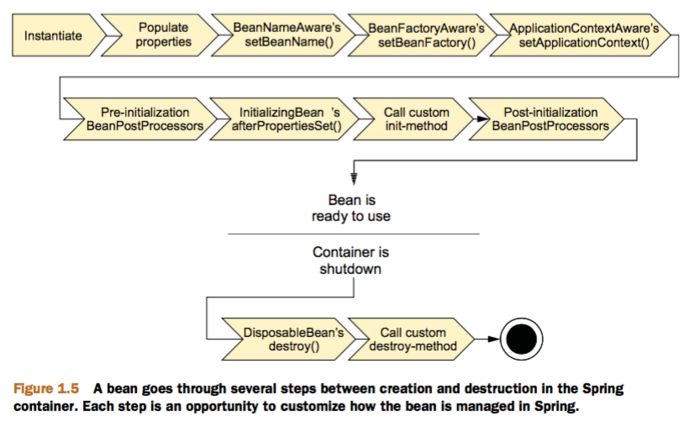
4.1 BeanNameAware
Spring Bean存活于容器之中,如果需要知道Bean的beanName,即可让该bean的类实现BeanNameAware接口
class UserBean implements BeanNameAware{
private String name;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
consumer.xml中注入bean
<bean id="aaa" class="com.aliyun.openservices.spring.example.normal.UserBean" >
</bean>
运行代码
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("consumer.xml");
UserBean userBean = context.getBean(UserBean.class);
System.out.println(userBean.getName());
这样控制台就能打印出结果,获取到UserBean的beanName是 aaa
4.2 ApplicationContextAware
该接口用于获取ApplicationContext的上下文,获取spring的一些信息
:::java
@Component
public class SpringBootTestAware implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext ;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext ;
}
}
这样我们就可以拿到ApplicationContext的对象做一些处理
4.3 InitializingBean
如果希望在bean的属性被创建后,做些额外处理,则可以考虑让这个bean实现InitializingBean接口。InitializingBean接口中的方法afterPropertiesSet()可以实现所需要的工作
在bean的声明周期中,afterPropertiesSet()方法的调用介于postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法和postProcessAfterInitialization()方法之间。
:::java
public abstract class AbstractFdxProcessor implements FdxProcessor, InitializingBean, BeanNameAware/*, BeanPostProcessor*/ {
//实现 BeanNameAware 接口,为了获得每个processor 在 Spring context 中的 beanName
//实现 InitializingBean 接口(Spring 提供的一些生命周期接口中的一个),在 Spring 完成该Bean初始化之后,将 beanName 注册到注册中心去
@Autowired
private FdxProcessorRegistry fdxProcessorRegistry;
protected String beanName;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
beanName = name;
}
protected abstract FdxProcessorRegistry.FdxKeyPair getKeyPair();
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
fdxProcessorRegistry.put(getKeyPair(), beanName);
}
}
@Service
public class XxxFdxProcessorImpl extends AbstractFdxProcessor{
@Override
public void process(FdxDto<?> fdxDto) {
//do business
}
@Override
protected FdxProcessorRegistry.FdxKeyPair getKeyPair() {
return new FdxProcessorRegistry.FdxKeyPair("XXX","XXX");
}
}
实际业务中,可以根据不同的beanName做缓存,然后路由到不同的业务,很适合if比较多的语句
4.4 自定义初始化和销毁方法
:::java
@Component
class StartAndDestroyBean {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StartAndDestroyBean.class);
@PostConstruct
public void start(){
LOGGER.error("init-method start");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
LOGGER.error("destroy-method start");
}
}
4.5 BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor接口则可以提供全局的、定制多个bean的初始化过程。BeanPostProcessor接口有两个方法:postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法在bean的属性值设置之前执行;postProcessAfterInitialization()方法在bean的属性值设置之后执行。
:::java
public abstract class AbstractFdxProcessor implements FdxProcessor, BeanPostProcessor {
//实现 BeanNameAware 接口,为了获得每个processor 在 Spring context 中的 beanName
//实现 InitializingBean 接口(Spring 提供的一些生命周期接口中的一个),在 Spring 完成该Bean初始化之后,将 beanName 注册到注册中心去
@Autowired
private FdxProcessorRegistry fdxProcessorRegistry;
protected String beanName;
protected abstract FdxProcessorRegistry.FdxKeyPair getKeyPair();
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
FdxCategory fdxCategory = bean.getClass().getAnnotation(FdxCategory.class);
//通过 fdxCategory 拿到 category, 作为 key 和 beanName 一起进入注册中心完成注册
return new Object();
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException{
return bean;
}
}
可以过滤出固定的bean做一些处理
4.6 DisposableBean
实现该对象,需要重写销毁方法
:::java
@Service
public class SpringBootTest implements DisposableBean{
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringBootTest.class);
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("destroy-method");
}
}
该方法会在自定义销毁方法前调用
[评论][COMMENTS]