1 实例化bean的主流程
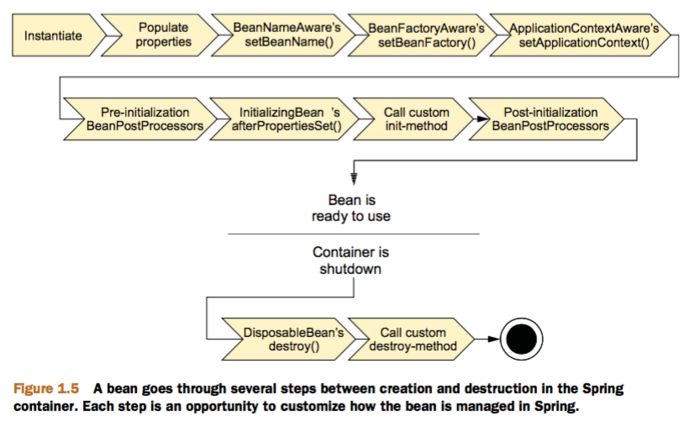
这张图是整体的bean的实例化的流程,我之前关于Spring的生命周期的加载bean和实例化bean的整体过程已有博文,可以 查看文章:Spring之Bean加载-解析-生命周期
调试入口
本文中的Spring源码基于3.2.x版本,为最精简的Spring源码,选取Spring自带的测试用例进行debug调试, 本文只关注单例对象的实例化bean中各组件的源码分析, 入口如下:
@Test
public void testConfigLocationPattern() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(CONTEXT_WILDCARD);
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("service"));
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("logicOne"));
assertTrue(ctx.containsBean("logicTwo"));
Service service = (Service) ctx.getBean("service");
ctx.close();
assertTrue(service.isProperlyDestroyed());
}
2 各组件流程
实例化bean的流程主要关注AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean方法,源码如下:
2.1 整体流程解析
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// BeanWrapper是对Bean的包装,其接口中所定义的功能很简单包括设置获取被包装的对象,获取被包装bean的属性描述器
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例模型,则从未完成的 FactoryBean 缓存中删除
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 使用合适的实例化策略来创建新的实例:工厂方法、构造函数自动注入、简单初始化
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 包装的实例对象
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
// 包装的实例对象的类型
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// 检测是否有后置处理
// 如果有后置处理,则允许后置处理修改 BeanDefinition
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
// 后置处理修改 BeanDefinition
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// 解决单例模式的循环依赖
// 单例模式 & 允许循环依赖&当前单例 bean 是否正在被创建
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 提前将创建的 bean 实例加入到ObjectFactory 中
// 这里是为了后期避免循环依赖 加入三级缓存删除二级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// 开始初始化 bean 实例对象
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 对 bean 进行填充,将各个属性值注入,其中,可能存在依赖于其他 bean 的属性
// 则会递归初始依赖 bean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
// 调用初始化方法
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// 循环依赖处理
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// 只有在存在循环依赖的情况下,earlySingletonReference 才不会为空
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// 如果 exposedObject 没有在初始化方法中被改变,也就是没有被增强
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
// 处理依赖
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 注册 bean
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
2.2 populateBean-递归填充bean的属性
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
// bean 的属性值
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
// 没有实例化对象
if (bw == null) {
// 有属性抛出异常
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 在设置属性之前给 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 最后一次改变 bean 的机会
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
// bean 不是"合成"的,即未由应用程序本身定义
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 将会阻止在此 Bean 实例上调用任何后续的 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 实例。
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
// 如果后续处理器发出停止填充命令,则终止后续操作
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
// 将 PropertyValues 封装成 MutablePropertyValues 对象
// MutablePropertyValues 允许对属性进行简单的操作,
// 并提供构造函数以支持Map的深度复制和构造。
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 根据名称自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
// 根据类型自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
// 是否已经注册了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
// 是否需要进行依赖检查
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
// 从 bw 对象中提取 PropertyDescriptor 结果集
// PropertyDescriptor:可以通过一对存取方法提取一个属性
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 这里会进行赋值处理,如通过 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理器处理注解 @autowired
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
// 依赖检查,对应 depends-on 属性
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
// 将属性应用到 bean 中
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
主要是获取需要注入的依赖bean,通过反射的方式将属性进行递归赋值
2.3 initializeBean方法之invokeAwareMethods
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
// 处理实现了aware接口相关类,调用方法
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
这部分也很简单根据Aware接口去对BeanNameAware , BeanFactoryAware 进行赋值
2.4 initializeBean方法之applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization-前置处理器
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
这部分源码主要是bean的前置处理,会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,我们关注下ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
这个类,它的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法会调用invokeAwareInterfaces方法,去执行其他基于Aware
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(
new EmbeddedValueResolver(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory()));
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法就在这里
2.5 invokeInitMethods-初始化方法
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
// 处理初始化方法 init-method
if (mbd != null) {
// 判断是否指定了 init-method(),
// 如果指定了 init-method(),则再调用制定的init-method
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
获取实现了InitializingBean的接口的bean,调用afterPropertiesSet方法处理,这里如果指定了init-method()方法,则还会执行相应的方法
2.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization-后置处理器
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
整体逻辑都很清晰,调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法去做后置处理
3 BeanPostProcessor注册
3.1 BeanPostProcessor的加载
前面分析了实例化调用各组件方法的流程,现在分析BeanPostProcessor的加载,具体在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法,
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 加载配置中的bean --> loadBeanDefinition方法
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 在实例化bean之前通过 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 最后一次机会对注册到该容器的 BeanDefinition 做出修改
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有遗留的非懒加载的单例对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}
整体流程就是加载xml的配置,会调动loadBeanDefinition方法,然后注册BeanPostProcessor,
发送事件,实例化非懒加载的bean。
registerBeanPostProcessors注册处理器的方法如下:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 获取所有的 BeanPostProcessor 的 beanName
// 这些 beanName 都已经全部加载到容器中去,但是没有实例化
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// 注册 BeanPostProcessorChecker,它主要是用于在 BeanPostProcessor 实例化期间记录日志
// 当 Spring 中高配置的后置处理器还没有注册就已经开始了 bean 的实例化过程,这个时候便会打印 BeanPostProcessorChecker 中的内容
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 按优先级别分组
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
OrderComparator.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
OrderComparator.sort(orderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
OrderComparator.sort(internalPostProcessors);
// 注册
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// 加入ApplicationListenerDetector(探测器)
// 重新注册 BeanPostProcessor 以检测内部 bean,因为 ApplicationListeners 将其移动到处理器链的末尾
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector());
}
这部分源码,主要是去bean容器中获取BeanPostProcessor的beanName,然后根据该处理是否实现了PriorityOrdered,Ordered的接口, 进行分类,最后按优先级别排序,注册到beanFactory中。
3.2 自定义BeanPostProcessor导致Spring事务失效问题
如果自定义BeanPostProcessor并实现了PriorityOrdered接口,会导致事务失效
例如:
public class WrappingPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@autowired
private Service service;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory(bean);
return pf.getProxy();
}
}
如果Service 这个类包含事务注解的方法,那么事务就会失效,原因是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个实现了 BeanPostProcessor的类的优先级别是Order级别,导致Service提前初始化
[评论][COMMENTS]