1 事务配置
关于Spring的事务,大家每天都会遇见或者用到,为了更好的理解Transaction的原理机制,我们从源码角度来解析,本文的调试源码基于Spring-3.2.x版本进行调试。
1.1 配置
配置XML文件annotationTransactionNamespaceHandlerTests.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd">
<tx:annotation-driven/>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.tests.transaction.CallCountingTransactionManager"/>
<bean id="testBean"
class="org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionNamespaceHandlerTests$TransactionalTestBean"/>
<context:mbean-export/>
TransactionalTestBean类
@Service
@ManagedResource("test:type=TestBean")
public static class TransactionalTestBean {
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Collection<?> findAllFoos() {
return null;
}
public void saveFoo() {
}
@Transactional("qualifiedTransactionManager")
public void saveQualifiedFoo() {
}
@Transactional
public void exceptional(Throwable t) throws Throwable {
throw t;
}
@ManagedOperation
public String doSomething() {
return "done";
}
@Transactional
protected void annotationsOnProtectedAreIgnored() {
}
}
上面XML配置主要是开启事务驱动,然后配置事务管理器和带有@Transaction注解的Bean对象
1.2 调试入口
public class AnnotationTransactionNamespaceHandlerTests extends TestCase {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setUp() {
this.context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"org/springframework/transaction/annotation/annotationTransactionNamespaceHandlerTests.xml");
}
@Override
protected void tearDown() {
this.context.close();
}
public void testIsProxy() throws Exception {
TransactionalTestBean bean = getTestBean();
assertTrue("testBean is not a proxy", AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean));
assertEquals("Should not have any started transactions", 0, ptm.begun);
bean.findAllFoos();
assertEquals("Should have 1 started transaction", 1, ptm.begun);
}
}
通过调用testIsProxy方法调试事务流程
2 事务解析
2.1 事务NameSpaceHandler解析
2.1.1 加载事务驱动
在加载XML文件的时候,会通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法来加载配置。
解析到改行的时候会调用BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseCustomElement方法来处理自定义命名空间处理器。
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// 获取 namespaceUri
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
// 根据 namespaceUri 获取相应的 Handler
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
// 调用自定义的 Handler 处理
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
通过spring.handlers的定义配置:
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx=org.springframework.transaction.config.TxNamespaceHandler
找到对应的处理器TxNamespaceHandler,然后进行解析。关于Spring扩展机制NameHandler可以找文章了解
2.1.2 注册初始化处理器
初始化事务处理器init方法
public class TxNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static final String TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = "transaction-manager";
static final String DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "transactionManager";
static String getTransactionManagerName(Element element) {
return (element.hasAttribute(TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE) ?
element.getAttribute(TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE) : DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME);
}
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
上面注册的三个解析器
TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser : 用于处理tx:advice/标签全局定义的事务
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser : 用于处理tx:annotation-driven/标签注解类型的事务
JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser : 用于处理JTA事务
这里我们关注AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser的解析,调用parse方法
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
String mode = element.getAttribute("mode");
if ("aspectj".equals(mode)) {
// mode="aspectj"
registerTransactionAspect(element, parserContext);
}
else {
// mode="proxy"
AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator(element, parserContext);
}
return null;
}
如果是proxy代理模式则会调用configureAutoProxyCreator方法:
private static class AopAutoProxyConfigurer {
public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
String txAdvisorBeanName = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME;
if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) {
Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSource definition.
// 创建注册TransactionAttributeSource的bean
RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition(
"org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource");
sourceDef.setSource(eleSource);
sourceDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef);
// Create the TransactionInterceptor definition.
// 创建TransactionInterceptor的bean
RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class);
interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource);
interceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef);
interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor definition.
// 创建BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的bean
RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
advisorDef.setSource(eleSource);
advisorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName);
if (element.hasAttribute("order")) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order"));
}
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef);
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource);
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName));
parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef);
}
}
}
这里的执行流程如下:
注册代理组件 –> InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator –> 用于创建bean的事务代理类
创建注册事务属性源的bean –> TransactionAttributeSource –> 用于解析注解的事务属性
创建注册事务拦截器的bean –> TransactionInterceptor –> 用于拦截事务注解的方法处理
创建注册事务advisor的bean –> BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor –> 用于处理Bean是否需要代理的逻辑
2.2 Bean的事务解析
2.2.1 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator事务代理类
- 1 类图
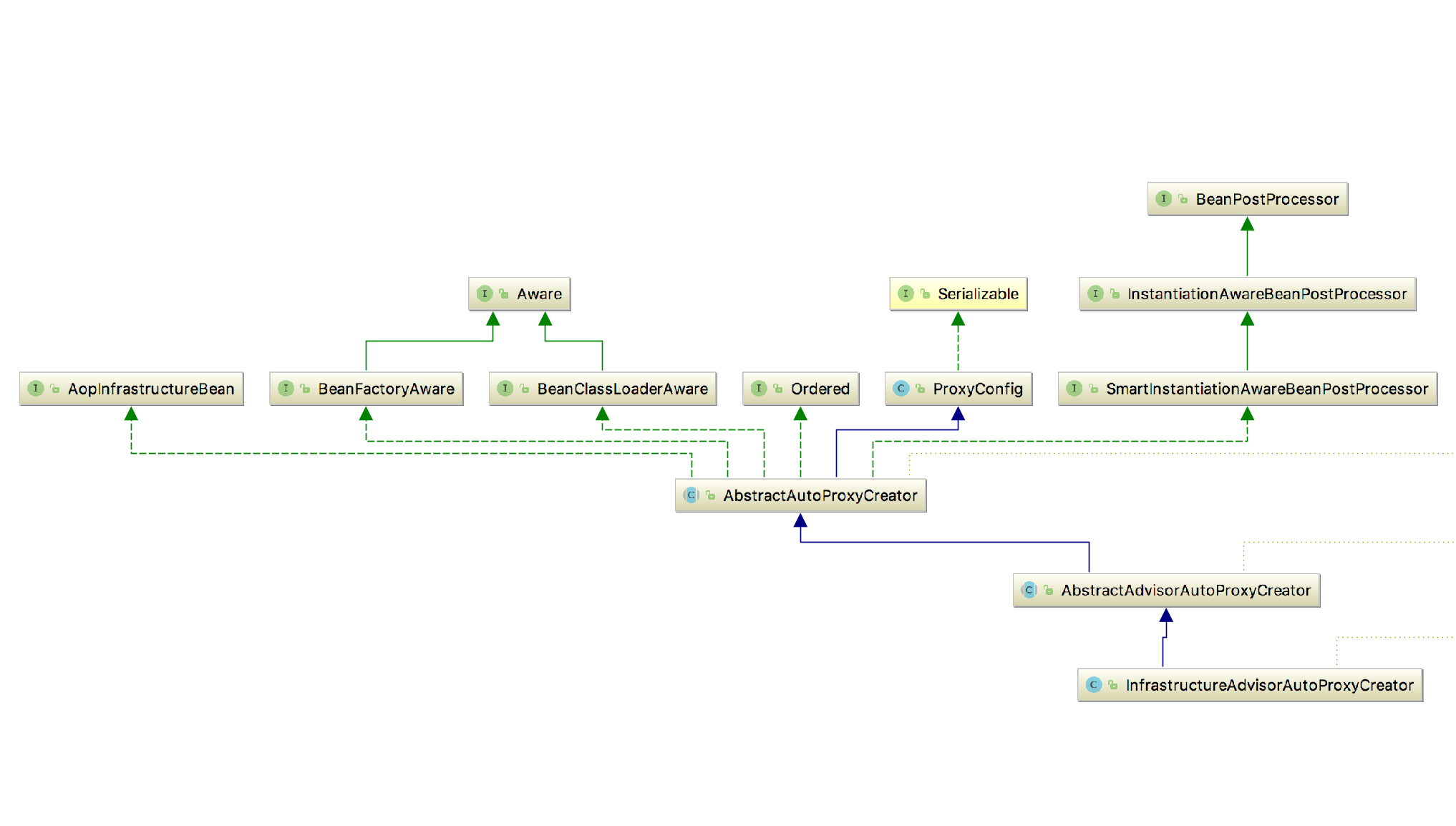
实现了Aware和BeanPostProcessor这两个类,所以在getBean的时候会用到前置处理器和后置处理器
为包含事务注解的Bean类创建代理的入口位于AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
// 获取缓存key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 如果不在map中就根据条件决定是否包装bean对象
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
wrapIfNecessary核心逻辑:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.containsKey(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 是否是基础类或者需要跳过的类
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 寻找适用于当前bean的Advisor并创建代理
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
当前的bean是否需要创建代理主要就是看getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean的方法逻辑
2.2.2 筛选Advisor确定是否需要代理
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的筛选符合条件的Advisor方法getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,最终
会调用:
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
// 查询Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 筛选符合条件的Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 用于对实现了Ordered接口的Advisor进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
上述的流程:
- findCandidateAdvisors –> 寻找实现Advisor接口的所有bean
- findAdvisorsThatCanApply –> 筛选符合条件的Advisor的bean
- extendAdvisors –> 扩展处理
- sortAdvisors –> 排序
重点我们需要知道筛选bean的流程findAdvisorsThatCanApply的方法逻辑中的canApply流程:
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// 判断advisor是否符合targetClass的切入点操条件
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
- 循环处理的判断逻辑:
- 如果
Advisor是IntroductionAdvisor,则判断对应的ClassFilter的matches方法是否匹配当前bean类 - 如果
Advisor是PointcutAdvisor,则先通过ClassFilter进行类匹配,如果匹配不成功,则通过MethodMatcher的matches方法进行方法匹配,只要bean有一个方法满足,则返回true匹配成功
- 如果
Spring事务相关的Advisor已经在之前TxNamespaceHandler.parse中已经注册过该bean。就是
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 这个类,具体的类图如下:
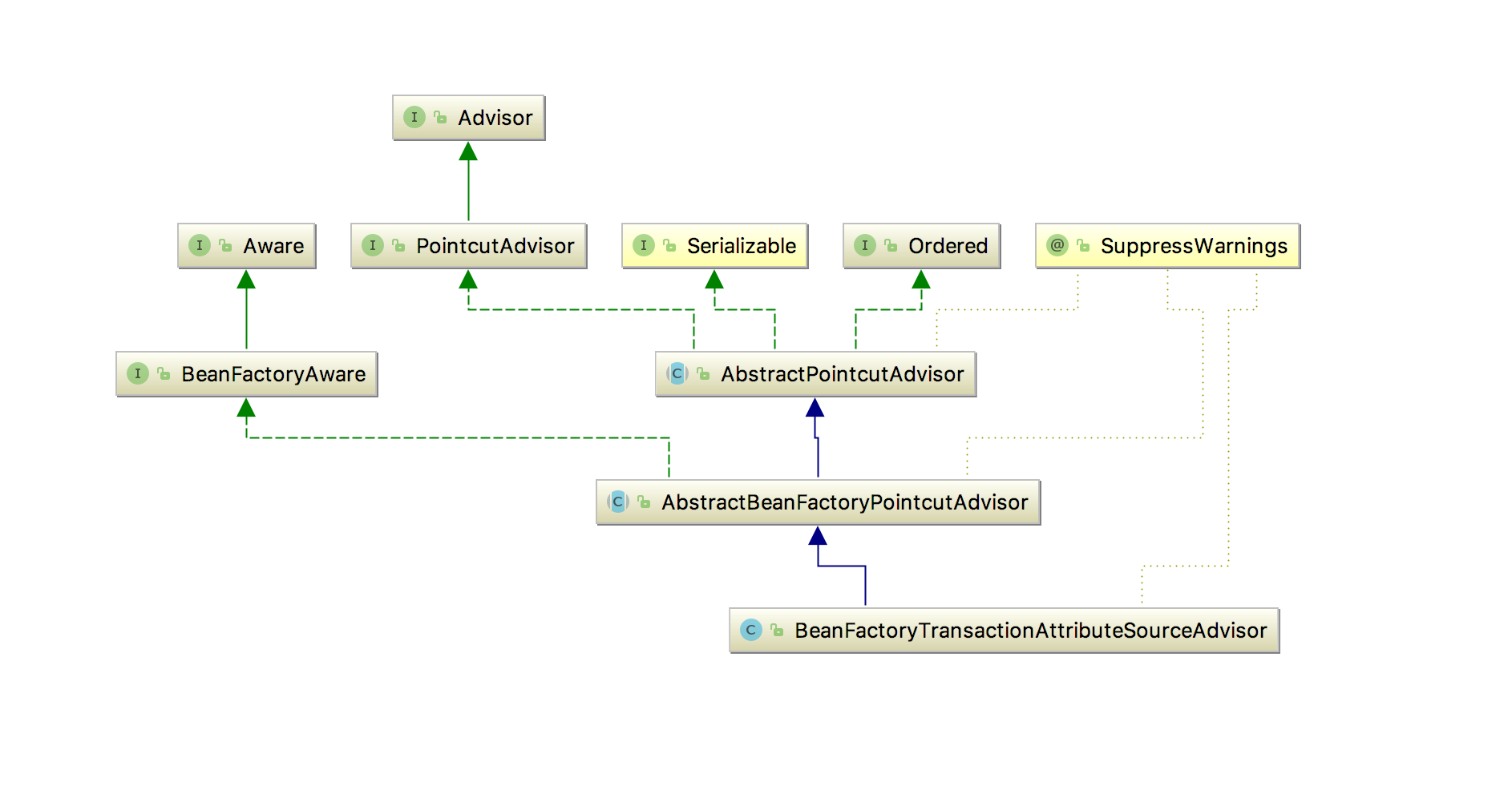
该类实现了Advisor接口,同时也是PointcutAdvisor的实现,通过pca.getPointcut()方法获取
Pointcut对象,具体实现是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut的类
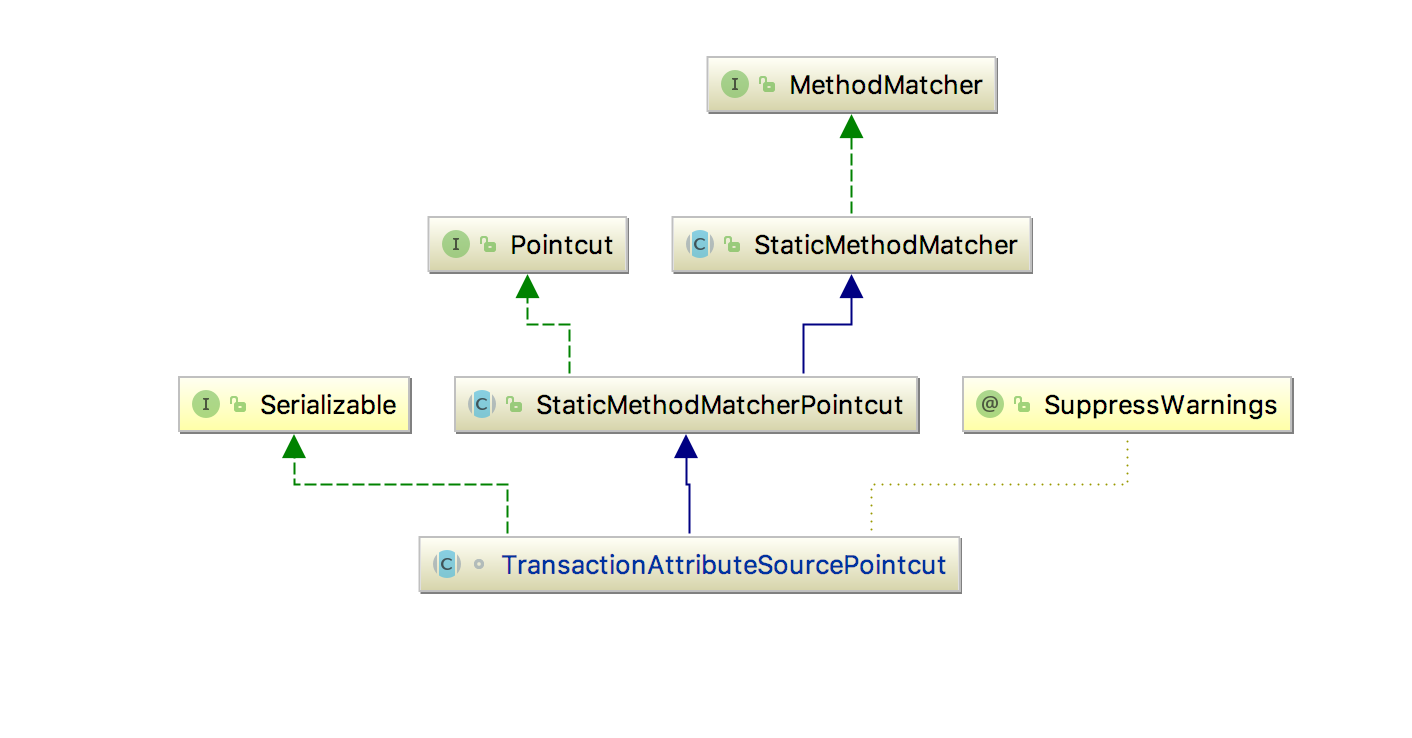
在调用pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)改方法,根据具体的实现,返回的永远是true,
所以最终进行方法匹配:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
//是否Pointcut可以匹配当前类
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
// 判断给定的方法是否在Pointcut匹配的范围内
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
上述代码逻辑中,introductionAwareMethodMatcher实例对象为空,所以通过methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)来匹配合适的方法,具体的实现逻辑如下:
public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) {
// 获取事务属性源
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
最终会调用AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource的computeTransactionAttribute方法来进行匹配:
private TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
// 不允许非public访问权限的方法代理
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// Ignore CGLIB subclasses - introspect the actual user class.
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass);
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, userClass);
// If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method.
// 如果我们处理的是一个泛型参数的方法,则获取他的桥方法
specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// First try is the method in the target class.
// 首先在方法上获取事务的属性
TransactionAttribute txAtt = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAtt != null) {
return txAtt;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
// 在类上获取事务的属性
txAtt = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAtt != null) {
return txAtt;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAtt = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAtt != null) {
return txAtt;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
return findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
}
return null;
}
上述流程主要通过findTransactionAttribut匹配:
- 1 首先方法上匹配,如果方法上有@Transaction注解则匹配成功,具体会通过SpringTransactionAnnotationParser这个解析器处理
- 2 其实类匹配,如果类上有@Transaction注解则匹配成功
- 3 如果是specificMethod != method,在按上述1和2的流程通过method去匹配
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser的代码如下:
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable {
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) {
Transactional ann = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(ae, Transactional.class);
if (ann != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(ann);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(Transactional ann) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(ann.propagation().value());
rbta.setIsolationLevel(ann.isolation().value());
rbta.setTimeout(ann.timeout());
rbta.setReadOnly(ann.readOnly());
rbta.setQualifier(ann.value());
ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollBackRules = new ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute>();
Class[] rbf = ann.rollbackFor();
// 回滚规则
for (Class rbRule : rbf) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
String[] rbfc = ann.rollbackForClassName();
for (String rbRule : rbfc) {
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
// 不需要回滚异常的规则
Class[] nrbf = ann.noRollbackFor();
for (Class rbRule : nrbf) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
String[] nrbfc = ann.noRollbackForClassName();
for (String rbRule : nrbfc) {
NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule);
rollBackRules.add(rule);
}
rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules);
return rbta;
}
}
就此,我们就可以判定Bean的方法中是否包含@Transaction这个注解,如果包含这返回这个对应Advisor,
即BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor这个实现,如果有这个实现那么
// 寻找适用于当前bean的Advisor并创建代理
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
就会创建bean的代理类
2.2.3 创建事务代理类
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
// 创建代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// Copy our properties (proxyTargetClass etc) inherited from ProxyConfig.
// 拷贝当前类中的相关属性
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//判定给定的bean是否代理Class
if (!shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to
// the target's interfaces only.
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, this.proxyClassLoader);
for (Class<?> targetInterface : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(targetInterface);
}
}
//将interceptor适配为Advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
// 设置目标类
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// 设置是否冻结,默认为false即代理设置后不允许修改代理的配置
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 创建代理
return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}
创建代理的主要目的就是将 Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors)的advisor集合放入到生成代理类的的AdvisedSupport advised变量中,在执行的时候会解析成Interceptor,然后调用,这边不具体展开。
[评论][COMMENTS]