1 事务还原
1.1 调试demo
我们使用常用的业务代码来做调试:
@Service("personService")
public class PersonServiceImpl implements IPersonService {
@Override
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,
rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void removeUserById(Integer id) {
personRepository.removeById(id);
User user = new User();
user.setId(0);
user.setName("aaa");
user.setSumScore("222");
user.setAvgScore("111");
user.setAge(20);
user.setIsSuccess(false);
user.setScore(UnsignedInteger.valueOf(1));
user.setStatus(UnsignedLong.valueOf(2));
userService.insertOne(user);
}
}
@Repository
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<Person, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor {
Person findByName(String name);
@Query("select p from Person p where p.id = ?1")
Person findObjectById(Integer id);
//@CacheEvict(value = "person")
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,timeout = 3)
void removeById(Integer id);
}
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
@Transactional
public void insertOne(User user) {
userDao.insert(user);
}
}我们通过以下测试用例,来调试事务相关信息:
@Test
public void doNothing() {
iPersonService.removeUserById(1);
}1.2 解析入口
// 事务开启
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// 继续执行剩下的advice调用链,最终执行本身方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常下提交或者回滚处理
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 还原前一个事务的信息到本地线程
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
这是一个事务的完整执行流程,事务预处理在上篇Transaction源码解析之事务预处理中已经详细解析过,现在我们来分析提交和回滚
1.3 还原上层事务
还原上层事务主要通过cleanupTransactionInfo方法处理:
private void restoreThreadLocalStatus() {
// Use stack to restore old transaction TransactionInfo.
// Will be null if none was set.
transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo);
}主要是将当前线程绑定为上一层的事务,比如在上述的测试代码中
personRepository.removeById(id)和userService.insertOne(user)是同一层事务,他们的上一层事务都是iPersonService.removeUserById方法的事务,这样做的目的是保证同一层事务提交完成之后,保证上一层的事务也得到处理,最终提交整个完整的事务
2 事务提交
事务提交主要关注commitTransactionAfterReturning这个方法,它最终会调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.commit的方法:
2.1 正常提交
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus);
return;
}
// 全局回滚的时候不commit并且当前事务需要回滚
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus);
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException only at outermost transaction boundary
// or if explicitly asked to.
if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
return;
}
// 处理提交
processCommit(defStatus);
}只要事务没有回滚,正常都会走processCommit(defStatus)的逻辑
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
// 准备提交
prepareForCommit(status);
// 触发提交前的同步器回调
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
// 触发完成前的同步器回调
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
boolean globalRollbackOnly = false;
if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
globalRollbackOnly = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
// 释放安全点
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
// 是否是新事务(最外层事务或者传播特性需要新建的事务)
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
// 提交
doCommit(status);
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (globalRollbackOnly) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
}catch (Error err) {
// 提交异常回滚
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, err);
throw err;
}
上述的代码主流程
准备提交
当前事务是否有安全点,有则释放
当前事务是新事务则提交
其他触发回调操作
所以只要当前事务不是新事务并不会提交,最终的doCommit提交就是数据库连接的提交将完成最终事务所有的处理
2.2 提交异常回滚
如果提交事务异常则会回滚:
private void doRollbackOnCommitException(DefaultTransactionStatus status, Throwable ex) throws TransactionException {
try {
if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback after commit exception", ex);
}
doRollback(status);
}
else if (status.hasTransaction() && isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Marking existing transaction as rollback-only after commit exception", ex);
}
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
}
}如果当前事务是一个新事务则直接回滚事务,如果当前事务存在则会将当前事务标记为rollbackOnly
3 事务回滚
3.1 回滚处理
事务出现异常则会根据策略进行回滚,方法在completeTransactionAfterThrowing中
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
// 是有存在事务
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.hasTransaction()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 是否需要回滚异常
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback error", ex);
throw err;
}
}
else {
// 不回滚
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit error", ex);
throw err;
}
}
}回滚的逻辑也很清晰:
是否存在事务,存在事务则进入回滚流程
判断回滚策略,是否需要回滚
不回滚则进入提交流程
如果需要回滚,最终进入processRollback方法:
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
try {
try {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
// 如果有安全点
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
// 回滚删除夯住的savepoint
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
// 是否是新事务(最外层事务或者传播特性需要新建的事务)
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
// 回滚
doRollback(status);
}
// 当前事务存在并且不是新事务
else if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
// 标记RollbackOnly
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
}上述逻辑主要分为三步
1 是否存在安全点,存在则删除安全点
2 是否是新事务,新事务则直接回滚数据库
3 如果有事务,但不是新事务则标记为需要回滚
3.2 回滚策略
主要关注RollbackRuleAttribute这个类,如果我们在使用注解@transaction的时候加入了rollbackfor属性指定了异常,则会生成对应的RuleBasedTransactionAttribute:
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Applying rules to determine whether transaction should rollback on " + ex);
}
RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (this.rollbackRules != null) {
for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {
int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);
if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {
deepest = depth;
winner = rule;
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Winning rollback rule is: " + winner);
}
// User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches.
if (winner == null) {
logger.trace("No relevant rollback rule found: applying default rules");
return super.rollbackOn(ex);
}
return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
}回滚策略主要是匹配指定的异常,如果没有指定的异常则会走父类的匹配策略
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}所以在默认情况下只有是运行异常或者Error错误才能回滚
4 事务执行完整流程
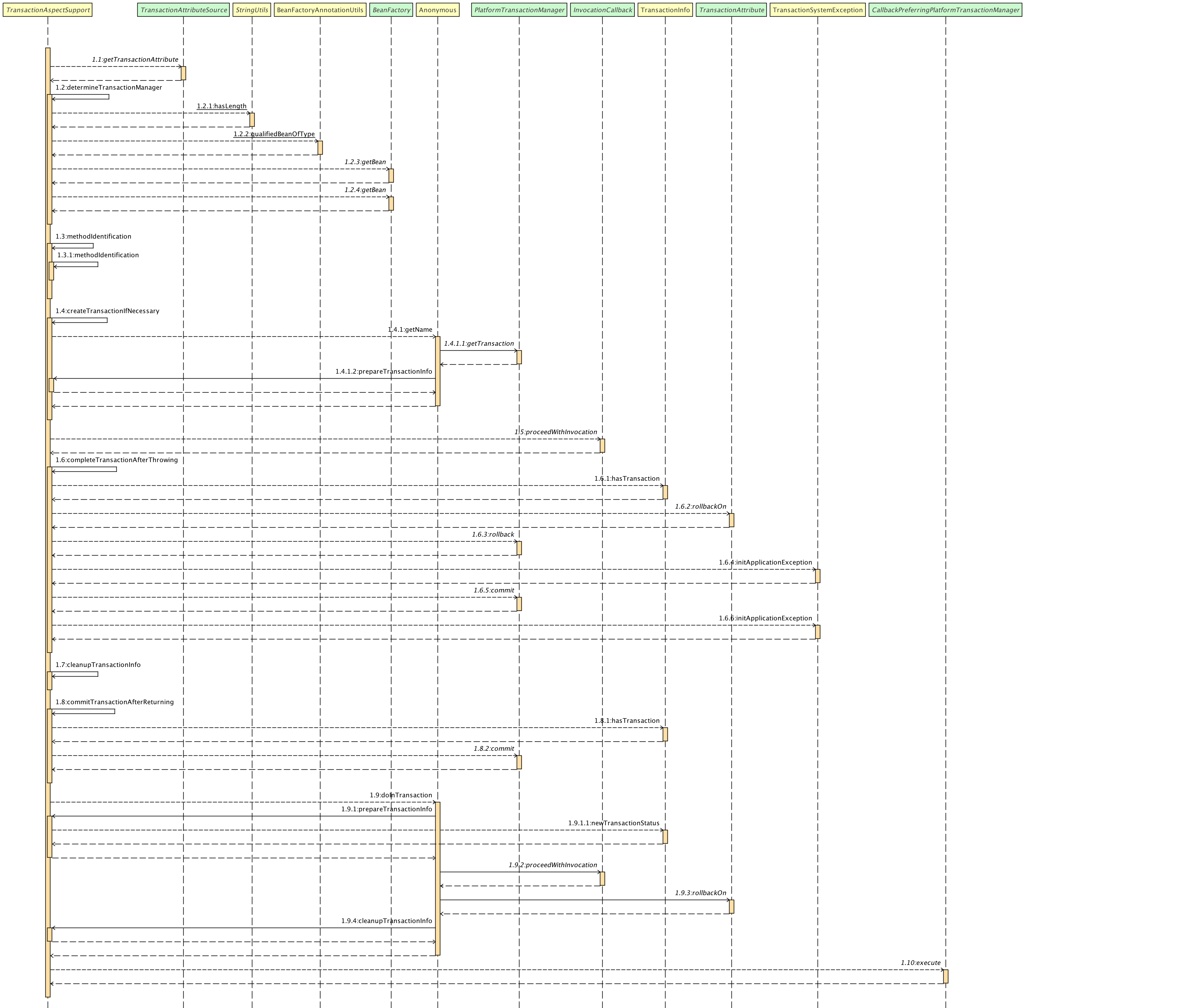
整体的时序图就是这样,所以removeUserById方法的事务执行就很好理解了,通过代理的方法递归提交事务,然后在事务最外层完成sql的最终提交
[评论][COMMENTS]